Fatty liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is becoming one of the most common liver conditions in the United States. Closely tied to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, this condition often progresses silently and can lead to serious complications if not addressed early. As the number of people struggling with obesity rises, so does the need for effective and lasting solutions. One of the most promising approaches to managing and potentially reversing fatty liver disease is bariatric surgery.
This blog explores how bariatric surgery can help treat fatty liver disease, what the procedure involves, and why it may be the right step for those dealing with obesity-related liver problems.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease and Its Risks
Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. It can be categorized into two main types:
NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease): Fat accumulates in the liver without any significant alcohol intake.
NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis): A more serious form of NAFLD, NASH involves inflammation and liver cell damage and can lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
NAFLD is strongly linked with obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure. These conditions are part of a group known as metabolic syndrome, which plays a key role in the development of liver disease.
Why Weight Loss Matters in Liver Health
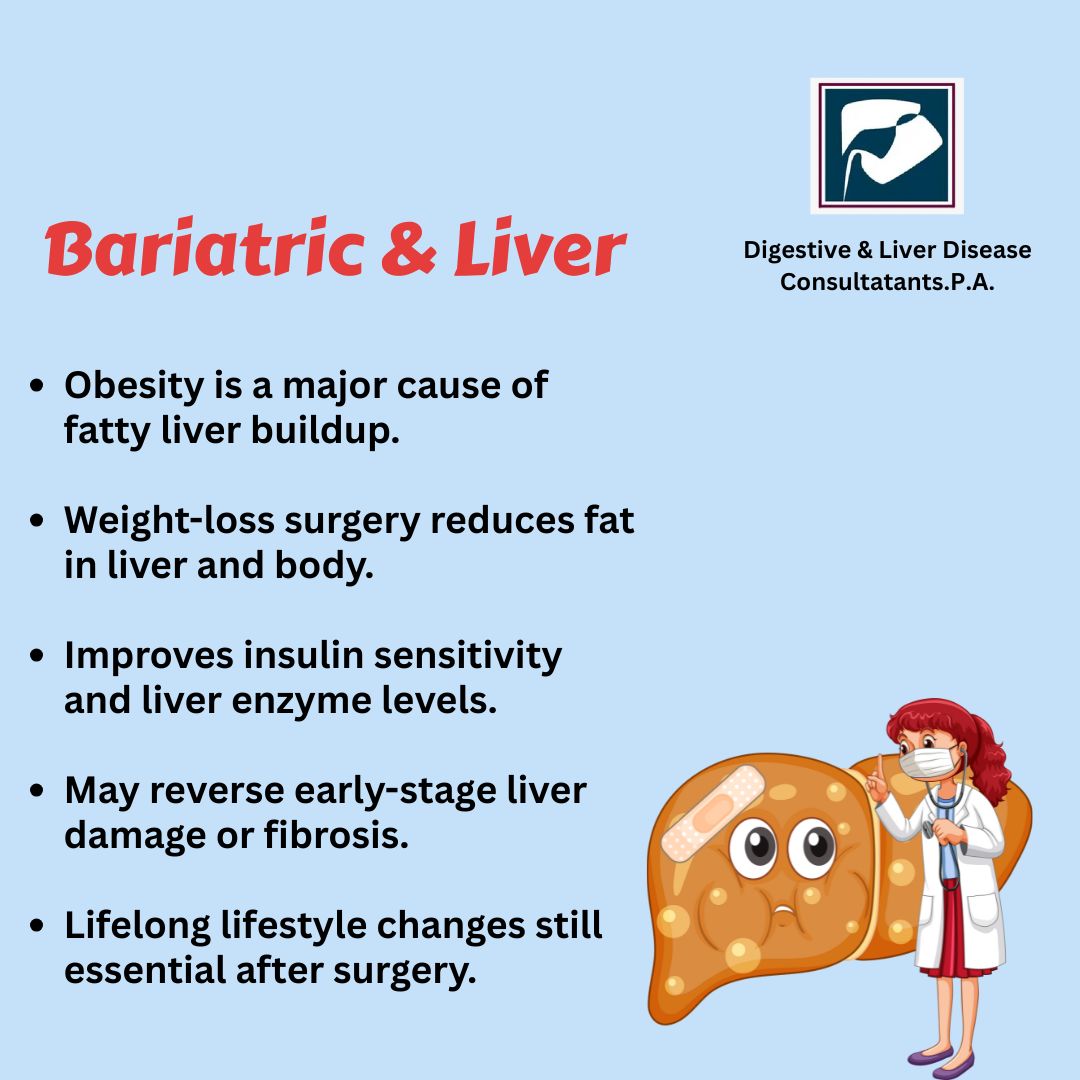
Weight loss is one of the most effective ways to reverse fatty liver disease. Research shows that even a modest reduction in body weight (about 5–10%) can significantly decrease liver fat, reduce inflammation, and improve liver enzyme levels.
However, for many individuals struggling with severe obesity, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise may not be enough. In such cases, weight loss surgery becomes a powerful tool in achieving long-term success.
Bariatric Surgery and Fatty Liver: How They’re Connected
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is a medical procedure designed to help patients lose excess weight by altering the digestive system. There are several types of bariatric procedures, but the most common ones include:
- Gastric bypass
- Sleeve gastrectomy
- Adjustable gastric banding
These procedures not only result in substantial weight loss but also trigger hormonal and metabolic changes that have a direct positive effect on the liver.
How Bariatric Surgery Helps in Treating NAFLD and NASH
Here’s how bariatric surgery benefits liver health and aids in the treatment of fatty liver disease:
1. Liver Fat Reduction Surgery
Post-surgery, patients often experience a significant drop in liver fat, which is crucial in treating both NAFLD and NASH. Imaging studies and liver biopsies show that fat content in the liver decreases dramatically within months after the surgery.
2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Obesity is associated with insulin resistance, which contributes to fat accumulation in the liver. Bariatric surgery improves insulin sensitivity, reducing fat deposition and slowing disease progression.
3. Reduction in Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis
In patients with NASH, weight loss surgery can help reduce liver inflammation and halt or even reverse early fibrosis.
4. Resolution of Metabolic Syndrome
Because bariatric surgery addresses metabolic syndrome, it helps improve cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and glucose control—all of which are key in preventing liver damage.
5. Long-Term Liver Health
Studies show that bariatric surgery is not just a short-term fix. Patients who undergo surgery have better long-term liver outcomes and a reduced risk of progressing to liver cirrhosis or requiring a liver transplant.
Is Bariatric Surgery Right for You?
Bariatric surgery is usually recommended for individuals who:
- Have a BMI (Body Mass Index) of 40 or more
- Have a BMI of 35 or more with obesity-related health problems like NAFLD, diabetes, or high blood pressure
- Have not had long-term success with other weight loss methods
If you are dealing with obesity and liver disease, you may be a good candidate for weight loss surgery.
Before undergoing surgery, patients undergo a detailed evaluation by a bariatric and liver specialist team. This includes liver function tests, imaging, and sometimes a liver biopsy to assess the extent of liver damage.
The Role of Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants, P.A.
At Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants, P.A., we specialize in comprehensive liver care. Our expert team understands the complex link between metabolic syndrome and liver health. We work closely with bariatric specialists to ensure that patients with fatty liver disease receive personalized, multidisciplinary care. Whether you're in the early stages of NAFLD or dealing with advanced NASH, we provide both medical and surgical options tailored to your needs.
Our goal is not just liver fat reduction but also to prevent the progression of disease and improve your overall well-being. We guide you every step of the way—from diagnosis and evaluation to treatment and ongoing follow-up.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery is emerging as a powerful treatment option for fatty liver disease. It not only promotes substantial weight loss but also significantly improves liver health, insulin resistance, and metabolic factors contributing to NAFLD and NASH. For individuals with obesity and liver problems, weight loss surgery offers hope for a healthier, longer life.
If you suffer from fatty liver disease or related conditions, don't wait. Schedule a consultation with our best gastroenterologist today and take the first step toward better liver health.